题目内容
自选一张图像,编程实现以下操作:
• 分别采用 Sobel 算子和 Canny 算子滤波,进行边缘提取;
• 显示原始图像以及不同滤波器滤波后的结果;
• 对于 Sobel 滤波结果,显示 x 方向的梯度、y 方向的梯度、梯度幅度、梯度角度等;
• 对于 Canny 算子滤波,显示滤波后边缘检测结果,并分析不同滤波结果的差异。
原理分析
Sobel 算子原理分析
Sobel算子是高斯导数的一般近似,是多用于边缘检测的离散性差分算子。
Sobel算子有两组不同的卷积因子
假设要对一张图中的( x,y ) 像素 (预设图片已处理为uint8格式) 使用Sobel算子,首先分别用两个卷积因子分别对该点做卷积。
x方向上的卷积为:
y方向上的卷积为:
那么,该点的梯度幅值和方向为:
如果梯度幅值G大于了阈值,那么这个点就可以被考虑成边缘点。
Canny 算子原理分析
Canny 算子是计算机视觉中应用最广泛的边缘检测算子之一。
Canny 算子进行边缘检测的步骤:
-
用高斯导数进行滤波降噪 现实中由于采集设备、环境干扰等多方面的原因导致采集到的图像信息都是含有大量噪声信息的, 高斯滤波可以将图像中的噪声部分过滤出来,使图像更平滑。
高斯滤波处理在图像上反映出来的是一个加权平均的过程,距离中心点越近的部分,其权重越大,反之越小,而权值的分布,则符合正态分布,对于一个二维图像来说,则符合二维高斯分布。 高斯滤波器(ksize = 5 , k = 2)的计算公式如下:
G[i,j]=\frac{1}{ 2πσ^2 } e^{-\frac{(i-k-1)^2+(j-k-1)^2}{2σ^2}} 计算获得高斯卷积核后,对图像进行卷积操作。
-
获得梯度的幅值与方向
利用上述[1. Sobel 算子原理分析],对平滑后的图像用Sobel算子进行卷积处理,获得图像的梯度幅值数组与方向数组。
-
非最大值抑制(NMS)
通俗意义上是指寻找像素点局部最大值,将非极大值点所对应的灰度值置为0,这样可以剔除掉一大部分非边缘的点。
首先要确定像素点C的灰度值在其8值邻域内是否为最大。
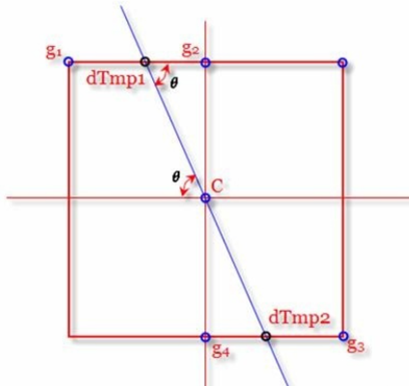
图1中蓝色的线条方向为C点的梯度方向,这样就可以确定其局部的最大值一定分布在这条线上,即出了C点外,梯度方向的交点dTmp1和dTmp2这两个点的值也可能会是局部最大值。
因此,判断C点灰度与这两个点灰度大小即可判断C点是否为其邻域内的局部最大灰度点。如果经过判断,C点灰度值小于这两个点中的任一个,那就说明C点不是局部极大值,那么则可以排除C点为边缘。
-
阈值化边缘:
-
设定双阈值(滞后阈值) T1>T2
- Step1: 当边缘像素强度>T1时,该边缘保留
- Step2:对T1>边缘像素强度>T2,当其与强边缘连接时才是边缘
- 找连通域(8个方向)
-
设计与实现
使用语言:Python 使用的库:opencv - python, numpy, matplotlib.pyplot 源码:test.py, main.py(见文件)
主要功能函数:
-
边缘补偿
def padding(image: np.ndarray, ksize: int) -> np.ndarray: '''在进行卷积操作前,对图像边缘进行补偿,避免边缘像素损失 ksize: 卷积核大小 pad: 需要补偿的边缘像素宽度 pad计算公式: pad = ksize//2 返回值: padded_out ''' h, w = image.shape[0], image.shape[1] pad = ksize//2 padded_out = np.zeros((h+2*pad, w+2*pad)) out_copy = image.copy() padded_out[pad:pad+h, pad:pad+w] = np.uint8(out_copy) return padded_out -
Sobel算子
def sobel_filter(image: np.ndarray): '''利用Sobel算子对图像进行卷积 sobelX = np.array([[-1, -2, -1], [0, 0, 0], [1, 2, 1]]) sobelY = np.array([[-1, 0, 1], [-2, 0, 2], [-1, 0, 1]]) 返回值: Gx:x方向梯度 Gy:y方向梯度 Ga:梯度幅度 theta:梯度角度 ''' sobelX = np.array([[-1, -2, -1], [0, 0, 0], [1, 2, 1]]) sobelY = np.array([[-1, 0, 1], [-2, 0, 2], [-1, 0, 1]]) pad = 1 h, w = image.shape[0], image.shape[1] tmp = padding(image, ksize=3) Gx = np.zeros([h + 2*pad, w+2*pad]) Gy = np.zeros([h + 2*pad, w+2*pad]) Ga = np.zeros([h + 2*pad, w+2*pad]) theta = np.zeros([h + 2*pad, w+2*pad]) for y in range(h): for x in range(w): #Gx[y + 1, x + 1] = np.sum(sobelX * tmp[y:y + 3, x:x + 3]) #Gy[y + 1, x + 1] = np.sum(sobelY * tmp[y:y + 3, x:x + 3]) Gx[y + 1, x + 1] = abs(np.sum(sobelX * tmp[y:y + 3, x:x + 3])) Gy[y + 1, x + 1] = abs(np.sum(sobelY * tmp[y:y + 3, x:x + 3])) Ga[y + 1, x + 1] = np.sqrt((Gx[y + 1, x + 1] ** 2 + Gy[y + 1, x + 1] ** 2)) if Gx[y + 1, x + 1] == 0: theta[y + 1, x + 1] = np.pi / 2 else: theta[y + 1, x + 1] = np.arctan(Gy[y + 1, x + 1] / Gx[y + 1, x + 1]) * 180/ np.pi #theta[y + 1, x + # 1] = np.arctan(Gy[y + 1, x + 1] / Gx[y + 1, x + 1]) Gx = Gx[1:1 + h, 1:1 + w].astype(np.uint8) Gy = Gy[1:1 + h, 1:1 + w].astype(np.uint8) Ga = Ga[1:1 + h, 1:1 + w].astype(np.uint8) theta = theta[1:1 + h, 1:1 + w].astype(np.uint16) return Gx, Gy, Ga, theta -
高斯模糊(平滑)
def gauss_filter(image: np.ndarray, sigma) -> np.ndarray: """计算高斯卷积核,填充图像并卷积滤波 高斯卷积核计算公式为: G(x,y) = (1/(2*pi*(sigma)^2))*e^(-(x^2+y^2)/2*sigma^2) 返回值: blur_img """ h, w = image.shape[0], image.shape[1] # 获得高斯卷积核 ksize = 5 k = ksize // 2 kernel = np.zeros([ksize, ksize]) for x in range(ksize): for y in range(ksize): kernel[y, x] = np.exp(-((x - k) ** 2 + (y - k) ** 2)/(2 * (sigma ** 2))) kernel /= (sigma * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi)) kernel /= kernel.sum() # 图像补边 tmp = padding(image, ksize) blur_img = np.zeros([h + 2 * k, w + 2 * k]) # 卷积计算 for y in range(h): for x in range(w): blur_img[y + k, x + k] = np.sum(kernel * tmp[y:y + ksize, x:x + ksize]) blur_img = blur_img[k:k + h, k:k + w].astype(np.uint8) return blur_img -
非极大值抑制
def NMS(Ga: np.ndarray, theta: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray: '''对梯度幅值进行非极大值抑制,凸显图像边缘 num_1,num_2:像素点Ga[i,j]梯度方向前后的经过插值运算获得的梯度值 若Ga[i, j]不是最大值,则该像素点归0 返回值: nms_img ''' h, w = Ga.shape[0], Ga.shape[1] nms = np.copy(Ga[1:-1, 1:-1]) for i in range(1, h-1): for j in range(1, w-1): angle = theta[i, j] weight = np.tan(angle) if angle > np.pi / 4: d1 = [0, 1] d2 = [1, 1] weight = 1 / weight elif angle >= 0: d1 = [1, 0] d2 = [1, 1] elif angle >= -np.pi / 4: d1 = [1, 0] d2 = [1, -1] weight *= -1 else: d1 = [0, -1] d2 = [1, -1] weight = -1 / weight g1 = Ga[i + d1[0], j + d1[1]] g2 = Ga[i + d2[0], j + d2[1]] g3 = Ga[i - d1[0], j - d1[1]] g4 = Ga[i - d2[0], j - d2[1]] num_1 = g1 * weight + g2 * (1 - weight) num_2 = g3 * weight + g4 * (1 - weight) if num_1 > Ga[i, j] or num_2 > Ga[i, j]: nms[i - 1, j - 1] = 0 nms_img = nms[0:h - 2, 0:w - 2].astype(np.uint8) return nms_img -
双阈值进行边缘的检测和连接
def threshold_edge(nms: np.ndarray, threshold_low: int, threshold_high: int) -> np.ndarray: '''强化图像边缘,去除无关细节 threshold_low, threshold_high: 设定的上下阈值 对图像进行遍历 若该像素点的幅值低于threshold_low,说明不是边缘点,去除,置为黑色 若该像素点的幅值高于threshold_high,说明是边缘点,加强,置为白色 返回值: output_img ''' visited = np.zeros_like(nms) output_img = nms.copy() h, w = output_img.shape[0], output_img.shape[1] def dfs(i, j): if i >= h or i < 0 or j >= w or j < 0 or visited[i, j] == 1: return visited[i, j] = 1 if output_img[i, j] > threshold_low: output_img[i, j] = 255 dfs(i - 1, j - 1) dfs(i - 1, j) dfs(i - 1, j + 1) dfs(i, j - 1) dfs(i, j + 1) dfs(i + 1, j - 1) dfs(i + 1, j) dfs(i + 1, j + 1) else: output_img[i, j] = 0 for y in range(h): for x in range(w): if visited[y, x] == 1: continue if output_img[y, x] >= threshold_high: dfs(y, x) elif output_img[y, x] <= threshold_low: output_img[y, x] = 0 visited[y, x] = 1 for y in range(h): for x in range(w): if visited[y, x] == 0: output_img[y, x] = 0 return output_img -
Canny滤波算子
def canny_filter(img: np.ndarray, threshold_low: int, threshold_high: int, sigma) -> np.ndarray: ''' canny滤波算子 返回值:smoothed_img, ga, nms_img, canny_img(前三者供比较) ''' # 高斯平滑 smoothed_img = gauss_filter(img, sigma) # sobel求导 gx, gy, ga, theta = sobel_filter(smoothed_img) # 非极大值抑制 nms_img = NMS(ga, theta) # 双阈值检测连接 canny_img = threshold_edge(nms_img, threshold_low, threshold_high) return smoothed_img, ga, nms_img, canny_img
实验结果
Sobel滤波结果
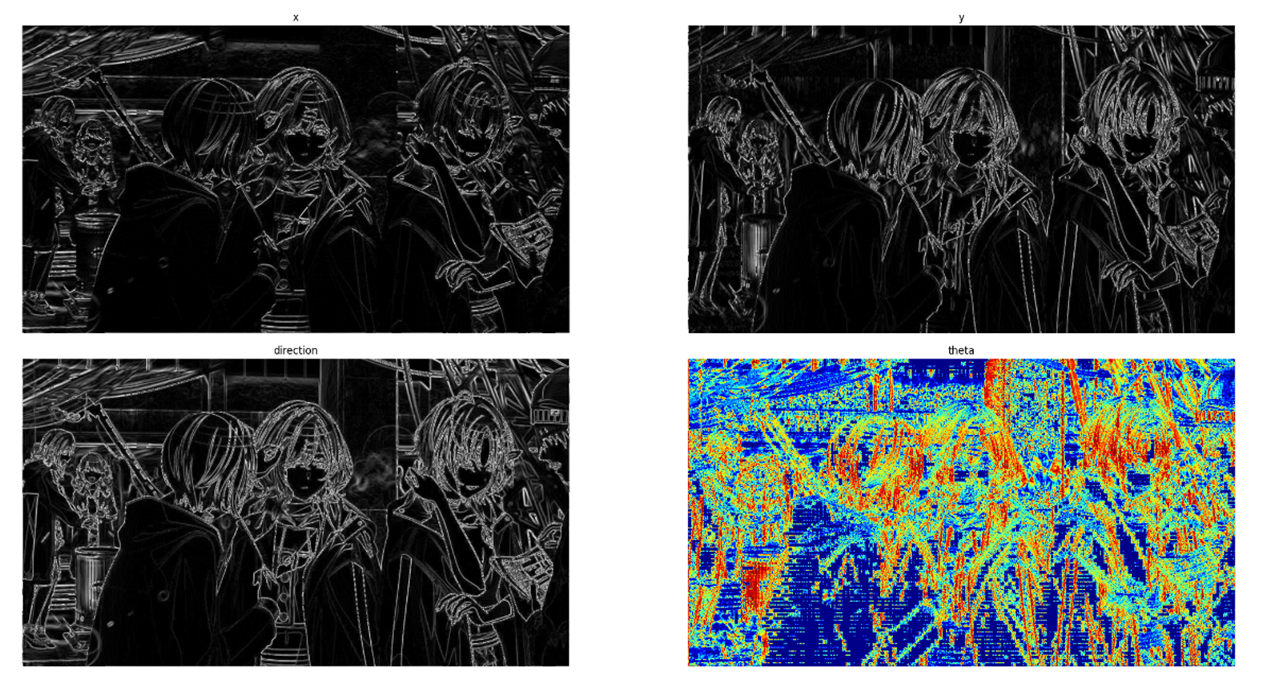
图像分析:原图以灰度模式读入后,x图,y图分别是sobel算子卷积后获得的图像在相应方向的导数值,会缺失另一个方向的边缘信息;direction图来自x,y两图像的各像素点平方和的根号,表示图像的梯度幅度,可视为sobel算子获得的边缘图;theta图像来自对direction各点的arctan值,范围为(-π,+π),用plt中的camp进行色彩映射。
Canny算子滤波结果
图像分析:原图在灰度模式读入后进行高斯模糊,获得更为柔和的smoothed_img,其中sigma对后续图像的细节留存量有影响,sigma越大,细节越少,当然也对噪点平滑力度更大;此时利用sobel算子求出图像梯度幅度,即ga图,噪点减少但图像边缘不够锐利;再进行非极大值抑制后获得nms_img, 图像边缘更加细致明确,但还有很多多余的细节;最后经过双阈值进行边缘检测与连接对重要边缘信息进行强化,所选的阈值范围决定筛选边缘信息的强度。


Comments | NOTHING